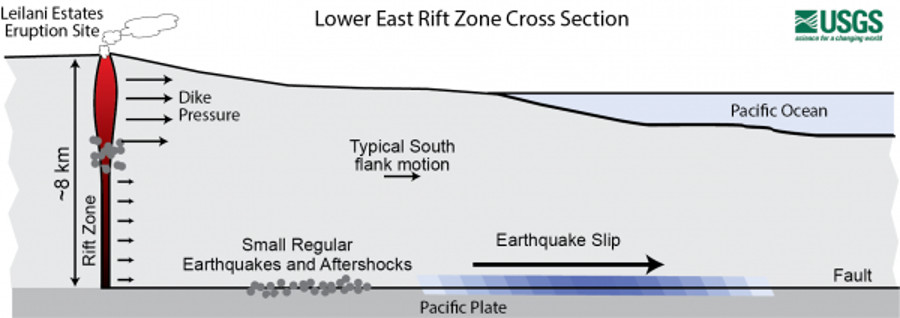
USGS Figure illustrating Kīlauea’s south flank motion and location of regular earthquakes and aftershocks. The fault depicted in the figure is the detachment fault or décollement. This figure illustrates how the 2018 lower East Rift Zone (LERZ) dike intrusion exerted pressure on the south flank.
(BIVN) – Following another Magnitude 4.1 earthquake that jolted the Puna district of Hawaiʻi island on Monday, scientists this week write about the seismicity on the south flank of Kīlauea volcano.
From the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory:
This story begins after Kīlauea’s May 4, 2018, M6.9 earthquake and lower East Rift Zone eruption. The M6.9 earthquake resulted in seaward motion at the surface of Kīlauea’s south flank of up to approximately 0.5 m (1.5 ft) as measured by Global Positioning System (GPS) monitoring stations operated by the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO).
Following the 2018 eruption, there was considerable contraction on Kīlauea’s middle East Rift Zone that was later followed by expansion or inflation as magma began refilling that area.
The south flank motion resulting from the M6.9 in 2018 was caused by motion deep below the surface, at depths of 7–9 km (4–6 mi), at the interface between Kīlauea Volcano and the ocean floor. This interface is known as a décollement or detachment fault. For more information on detachment faults, read this volcano watch article.
During the 1983–2018 Puʻu ʻŌʻō-Kupaianaha eruption, and prior to the 2018 M6.9 earthquake, the average rate of motion on Kīlauea’s south flank was around 8 cm (3 inches) per year. The flank can move faster or slower, depending on the time period and type of activity on the volcano. Rates can be variable but often remain near-constant during long-duration eruptions, with short-term changes during major rift intrusions and slow-slip earthquakes. For more information on slow-slip earthquakes, read this Volcano Watch.
Since the activity in 2018, there has been roughly 10 centimeters (about 4 in) of adjustments along Kīlauea’s south flank surface in the last two and a half years. This amount is to be expected and is nothing to be alarmed about.
The motion following the 2018 M6.9 earthquake and eruptive activity was caused by the magmatic intrusion in Kīlauea’s East Rift Zone exerting pressure on the south flank. The volcano adjusts after the combined effects of both the intrusion along the East Rift Zone and the large earthquake.
Following the M6.9 and 2018 eruption, Kīlauea’s East Rift Zone had been showing inflation consistent with magma supply to the volcano’s shallow magma storage system. However, at the start of Kīlauea’s ongoing summit eruption in December 2020, the upper portion of the East Rift Zone started to show signs of contraction. GPS stations along the upper and middle parts of the rift zone started to move northward, which is a rare occurrence on such a short timescale. This was occurring while Kīlauea’s summit was deflating at the onset of the eruption.
Kīlauea’s south flank’s response to changing magma pressure has been studied extensively through many previous eruptions and intrusions. For example, the 2007 middle East Rift Zone “Father’s Day” intrusion also led to a slight contraction of the rift zone following the intrusion and subsequent eruption. For more information on the Father’s Day intrusion and eruption, read this volcano watch.
It’s also common to see elevated rates of motion on faults after large earthquakes. Kīlauea’s south flank was the site of 5 earthquakes of magnitude 4.0 or greater in the past year. The M4.1 earthquake this past Monday, February 1, 2021, beneath the south flank is one of the five and it was felt across the Island of Hawaiʻi. These earthquakes happen in response to abrupt motion of the detachment fault which moves to the southeast over the oceanic crust. The abrupt motion releases pressure on the south flank that is caused by magma accumulation beneath the surface.
The relationship between tectonics and volcanism of the Hawaiian Islands is widely studied and the story of Kīlauea’s south flank continues to unfold in time. HVO’s dense monitoring network of GPS stations allows us to closely monitor and report these changes, while also giving us the opportunity to learn more about the volcano’s behavior.


by Big Island Video News7:28 am
on at
STORY SUMMARY
HAWAIʻI ISLAND - The USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory writes about the uptick in earthquakes over the last three years.