KALAPANA, Hawaii – The front of the 61g lava flow was about 0.7 miles from the ocean as of mid-day July 7, and was moving “at a good clip”, report scientists from the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory.
Last week, the lava flow reached the base of the Pulama pali and initially moved across the coastal plain at a rate of up to about 0.4 miles per day, which scientists say is fairly rapid compared with other Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō pāhoehoe flows.
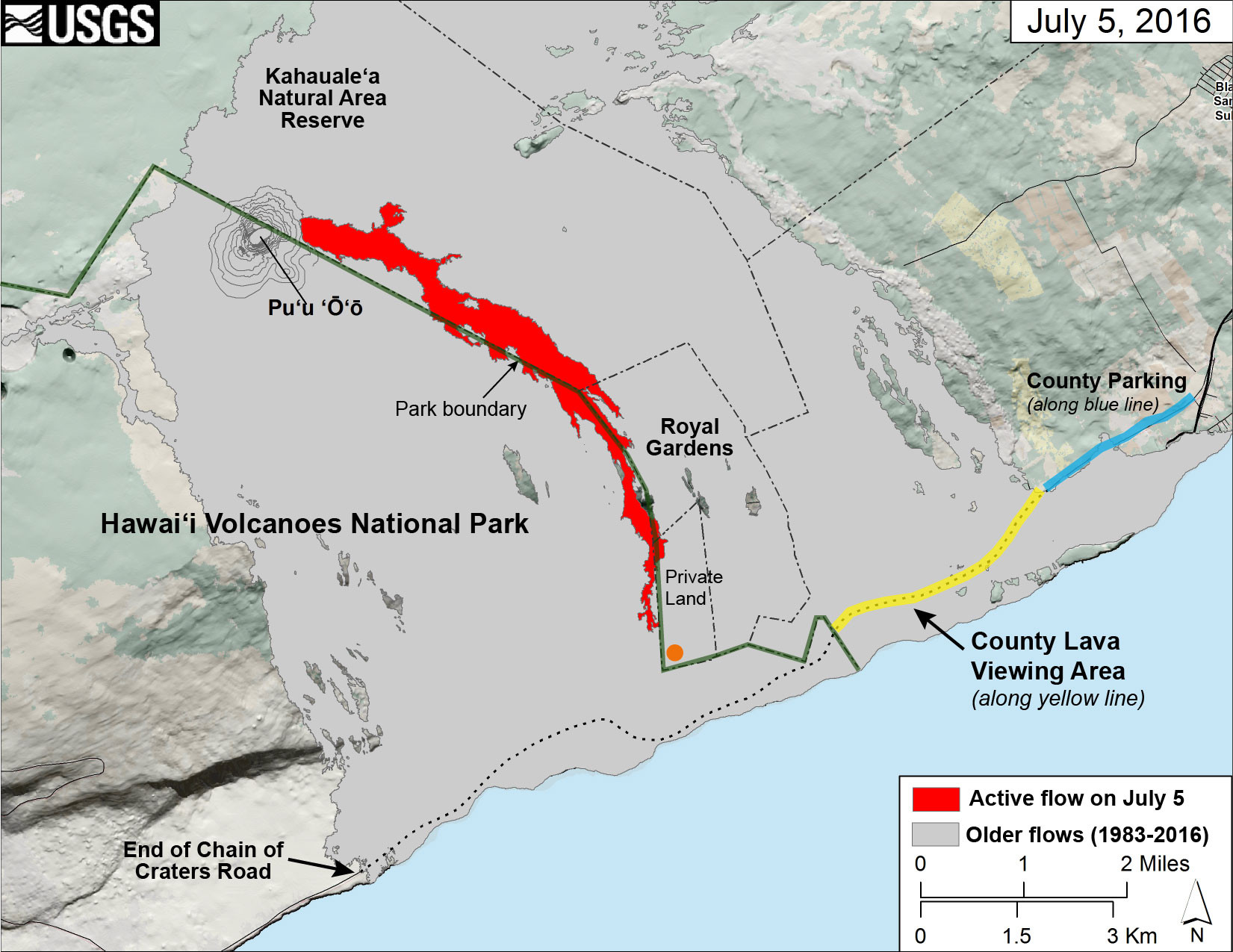
This map of Kīlauea Volcano’s lava flow shows the locations of Hawaiʻi County’s designated lava-viewing and parking areas (http://www.hawaiicounty.gov/lava-viewing/), as well as the lava flow’s location relative to the Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park boundary (green line). The full extent of the active lava flow on July 5 is shown in red; an orange dot shows the location of the flow front as of mid-day on July 7. For recent maps and photos of the lava flow, please visit the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory website. USGS graphic.
“Given the flow’s current advance rate,” reads the latest Volcano Watch article from the USGS HVO, “lava could reach the ocean for the first time since August 2013 in the coming days or weeks. However, the flow’s advance could slow, spreading lava across the coastal plain rather than into the ocean, or it could stall.” The full Volcano Watch article is below.
Videographer Mick Kalber captured more video from above thanks to Paradise Helicopters, reporting “Pele continues to move across the coastal flats, widening the flow field and making steady headway toward the ocean.” Kalber’s footage shows just how close the lava is to the emergency access road linking Highway 130 in Kalapana to the Chain of Craters Road in Hawaii Volcanoes National Park.
VOLCANO WATCH
Volcano Watch is a weekly article and activity update written by U.S. Geological Survey Hawaiian Volcano Observatory scientists and affiliates.
VOLCANO WATCH – 07 July 2016Kīlauea Volcano’s Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō lava flow advances toward the ocean
Two years ago, Kīlauea Volcano’s “June 27th” flow advanced to the northeast, threatening Pāhoa and creating major disruptions to thousands of residents in the lower Puna district on the Island of Hawaiʻi. Today, a new flow from Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō is moving to the southeast along the boundary of Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park and could eventually reach the ocean.
As Hawaiʻi residents can appreciate, change is just part of the typical behavior of Kīlauea’s ongoing East Rift Zone eruption.
This new lava flow, informally dubbed the “61g” flow after the eruptive episode sequence the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory uses to document Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō flows, began on May 24, 2016. Over the past six weeks it has advanced to the southeast without interruption. The flow has remained relatively narrow and focused, and consists mostly of pāhoehoe lava, which is typical of Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō flows in recent years.
Around June 23, the 61g flow reached the top of the pali (cliff) above the coastal plain and the upper boundary of the abandoned Royal Gardens subdivision, which is almost completely buried by earlier Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō lava flows. As the flow continued to advance, it picked up speed on steep sections of the pali, forming impressive ‘a‘ā lava channels on the slopes.
Within a few days, the flow front reached the base of the pali and began its advance across the coastal plain. There, the flow front narrowed even more, perhaps because it was confined by nearby high ground created by earlier Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō flows. This focusing of the flow probably contributed to its high advance rate on the coastal plain.
The 61g flow front initially moved across the coastal plain at a rate of up to 600 m (about 0.4 mi) per day, which is fairly rapid compared with other Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō pāhoehoe flows. As of mid-day on July 7, the flow front was about 1.2 km (0.7 mi) from the ocean, and still moving at a good clip. Given the flow’s current advance rate, lava could reach the ocean for the first time since August 2013 in the coming days or weeks. However, the flow’s advance could slow, spreading lava across the coastal plain rather than into the ocean, or it could stall.
Compared to the June 27th flow, which threatened Pāhoa and nearby subdivisions, the location of the 61g lava flow presents no immediate hazard to residential areas. It is currently overrunning older Pu‘u ‘Ō‘ō lava flows a safe distance from the nearest homes.
Although the hazard to property has diminished, the potential hazard to people is greater now that the flow is more accessible. The opportunity to see an active lava flow is already drawing hundreds of visitors hoping for a glimpse of lava to Kīlauea’s south coast.
Besides the obvious dangers of molten lava (burns, exposure to fumes), hiking to a lava flow is risky for a number of reasons, including the possibility of falling on the rough, uneven terrain, becoming dehydrated, or suffering heat exhaustion or stroke. Heat from above (the sun) and below (hot ground) can rapidly overwhelm even the strongest of hikers. Proper gear—sturdy hiking boots, long pants, gloves, sun protection—and LOTS of water are essential for safe hiking.
If lava reaches the sea and forms an ocean entry, new hazards will appear. In general, ocean entries are the most dangerous part of a lava flow field due to unpredictable bench collapses, explosions, and scalding steam plumes. This danger is not theoretical—several people have died near Kīlauea ocean entries in years past.
To safely view the 61g flow, your best plan is to get up-to-date lava-viewing information from Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park and the County of Hawaiʻi. These agencies have outlined where and when safe lava viewing is available.
The U.S. Geological Survey offers information on viewing lava safely in an online Fact Sheet. Because it was published in 2000, the map is out of date. However, the hazard information and safety tips provided in the Fact Sheet are timeless and relevant.
From home, you can track the progress of Kīlauea’s lava flow through daily eruption updates and recent maps and photos posted on the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory website.


by Big Island Video News12:32 am
on at
STORY SUMMARY
KALAPANA (BIVN) - Mick Kalber's latest video above the flow aboard Paradise Helicopters shows the proximity of the lava to the emergency road... and the ocean.